If you have just started playing video games then it is most probable that you have seen the option of ‘VSync’ in your settings. This will also show up if you work with 3D graphics.
To understand what is VSync, first, let us try to understand how your system processes graphics that are seen your screen. Your system utilizes an integrated graphics program that is within your CPU, or from an outsourced graphics card.
The graphics processor guides your screen to draw a particular image so that it is visible to you clearly.
See More: How to Get Better Gaming Performance From Your Computer
What is VSync? What does “VSync On” mean?
The graphics processor renders, let us say for example a 3D scene through ‘frames’ as quickly as possible. These frames are then processed by the monitor, again frame by frame.
The rate at which the graphics processor can output the frames is called “frames per second,” or FPS for short. More the frames your graphics processor can output, the smoother will be your gaming experience.
Most problems arise when the graphics processor begins to give out more frames per second than your monitor can handle. So basically the speed of receiving and processing the frames varies.
Your monitor then may struggle to keep up with the flow and end up being out of sync between two frames. This results in the picture being fragmented or torn apart.
We call this “screen tearing,” where an image is distorted.
You are therefore likely to see two images partly at the same time. This kind of split display is called screen tearing. It makes the image look like it has been broken into two parts.

So VSync or Vertical Sync is called a display feature and is mostly found in 3D video games. This allows a gamer to synchronize the frame rate of the game with the monitor refresh rate. The result is a great visual synchronicity and a good gaming experience.
VSync makes sure that GPU does not send any frame while the screen is engaged in displaying a previous frame. It achieves this via primarily two processes called double buffering and triple buffering.
When the computer wants to show something on a monitor, it draws an image what is to be displayed on the screen and sends that image. This is called ‘buffer’ which is not yet shown on the screen to the monitor.
Single Buffering
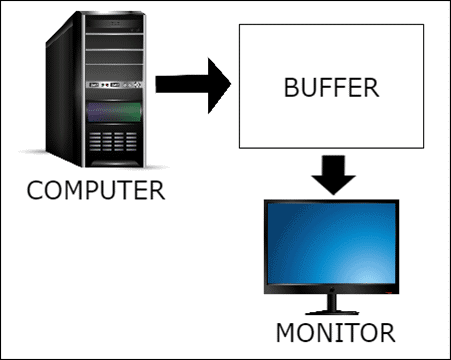
Previously it was the only single buffer that supposed to be continually drawn and sent to the monitor. However, with the single buffer approach, there are some drawbacks like flickering image on the screen. Therefore to counter this double buffering was preferred.
Double Buffering
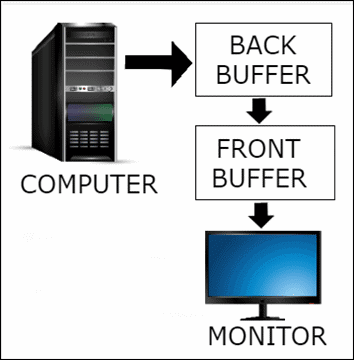
Double buffering consists of two buffers called “Front Buffer” and “Back Buffer”.
In double buffering, the computer only draws one buffer (back buffer) and sends the other buffer (front buffer) to the screen. Now, when the computer completes drawing back buffer also, swapping happens.
The front buffer becomes the back buffer and Vice Versa. In this same manner, the drawing program keeps drawing the new back buffer. The front buffer goes on screen and the new back buffer becomes the new front buffer. This kind of swapping goes on all the time.
Triple Buffering – VSync
Double buffering disappoints the viewer when you have to make a choice between two critical situations. With double buffering you experience screen tearing without VSync.
If VSync is enabled to avoid Screen Tearing, a significant delay will happen that may affect performance and increase input lag.
The Triple buffering will resolve both the problems that will enhance the overall performance.
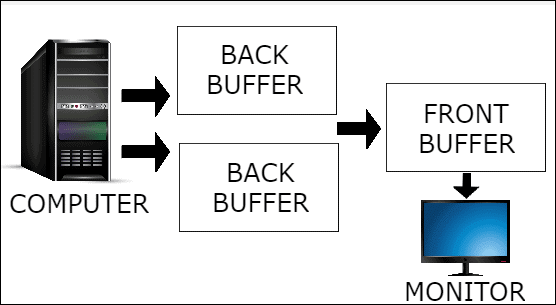
As the name suggests, in triple buffering there are two back buffers used. The second back buffer is added to avoid screen tearing and to increase the performance. In triple buffering, first, the GPU renders a frame in one back buffer. Secondly, while waiting for a swap to happen with the front buffer, it can instead start rendering the second back buffer.
Although with triple buffering you may need to have a modern graphics card. You also need to have access to a higher memory space.
There are various alternatives for VSync like Nvidia G-Sync, AMD FreeSync, and AMD Enhanced Sync.
VSync – The Pros and Cons
VSync is a must if you are experiencing screen tearing as it manages the coordination between the graphics processor and monitor. The speed and output levels between your processor and the monitor will be on the same level that will help to avoid screen tears.
When you prefer to play older video games VSync can be a good option. This is because the graphics processors work very fast. Then dealing with old screens may result in exceptionally high frame rates.
Due to the high frame rate, the graphics processor may overheat. When and if VSync is enabled, it will match the frame rate to the monitor’s refresh rate. This will avoid the high pressure on the graphics processor.
So VSync avoids screen-tearing, but it may also introduce lags since the GPU has to wait for the screen to get ready. When the frame is displayed finally it may also affect the frame rate if the GPU is not able to match with the screen’s refresh rate.
You can experience that keypress and mouse click are delayed with VSync-enabled and your actions will be delayed and less-responsive than before.
Types of VSync in the Market
Nvidia Adaptive Vsync
Frame rate stuttering and screen tearing are bad experiences while gaming. Adaptive sync is a unique feature that found in Nvidia. When the frame rate exceeds the monitor refresh rate, it immediately switches it off every time your fps comes below your monitor refresh rate. It prevents lagging so that you can continue playing your favorite online game.
Nvidia Smooth Vsync
This one is also exclusive to Nvidia that minimizes the stuttering. Your game runs at a specific frame rate, Smooth VSync maintains that frame rate and increases it while making it sure that GPU can sustain that frame rate without dropping. This may lower the average framerate of your game, but give you a better gaming experience in most of the cases.
Nvidia G-Sync
With G-Sync all your games are rendered in a smooth and sharp way. It is a game-changing technology with a refresh rate from zero to 240 Hz and gives an unbelievable performance. It eliminates stuttering by dynamically matching the refresh rate of the display to the frame rate of the GPU. The refresh rate supports from zero Hz to the maximum that your LCD panel supports.
AMD FreeSync
AMD FreeSync technology eliminates the inconsistencies in the gameplay. It delivers dynamic refresh rates that synchronize the rate of a compatible monitor to the frame rate of the user’s Radeon graphics that reduces the input latency and eliminates stuttering.
AMD Enhanced Sync
AMD Enhanced Sync enables low latency gameplay at virtually any frame rate while rendering you tear-free experience when the game’s frame rate exceeds the display’s refresh rate. It minimizes screen tearing while decreasing the latency and stutter of traditional VSync.
You can see the example image below for AMD Enhanced Sync.


Should you turn VSync On or Off?
Well, it doesn’t help you stick to a conclusion whether you should turn it ON or not. It all revolves around what your case is. Suppose if your graphics processor is rendering more frames that your monitor cannot handle, it will turn up the heat and cause screen tearing.
In this case, enabling VSync is helpful. If your frame rate is lower than your monitor’s refresh rate, there is no use of having VSync ON else it will only cause your system to become less responsive.
Well, it’s quite easy to turn VSync ON and OFF depending on the graphics card you have. If you are wondering how to turn on Vsync, then you have to go to your graphics processor settings and turn on the VSync.
Settings differ depending on which graphics processor you have. You can experience both by switching VSync ON and OFF to see how it affects your system so that you can consider it keeping it the way your system is okay with.
Conclusion
Perhaps, now that you are clear about what is VSync and whether to keep it on or off, you can trust your own judgment. So go ahead and experiment with it.
Further Reading: 8 Ways to Protect Your Eyes in Our Screen-Centric World







