Key Takeaways
- If you face any issues with your PC, you can boot it into safe mode in Windows 11
- Safe mode starts Windows in a basic state with minimal features
- You can choose to enter minimal safe mode, safe mode with networking, and safe mode with command prompt
If you work a lot on your computer, you must be familiar with the dedicated safe mode in Windows 11. System crashes that result in the infamous blue screen can be subjected to troubleshooting in safe mode. Driver faults and many other hardware issues can cause booting problems in your PC. When you start the device in safe mode, the basic state is loaded, where you still have access to critical drivers and files.
If the safe mode works fine, ensure there are no issues with the basic device drivers and default settings. Once the system is in this mode, you can troubleshoot, find the real issue, and tackle it. If you cannot access the internet in safe mode, find solutions for Windows 11 safe mode with networking no internet issues.
How To Boot Into Safe Mode In Windows 11
When you start safe mode in Windows 11, you can enter minimal safe mode, safe mode with networking, and safe mode with Command Prompt.
You can choose the one that meets your requirements. So, read on and discover the ways for Windows 11 safe mode boot process.
1. Using the Start Menu
Even though there are various methods to enter safe mode in Windows 11, opening the Start menu and pressing Shift + Restart is considered the easiest. Here are the steps to do it.
First, open the Start menu and keep the Shift key pressed. Next, click the Power button in the lower-right corner and “Restart.”
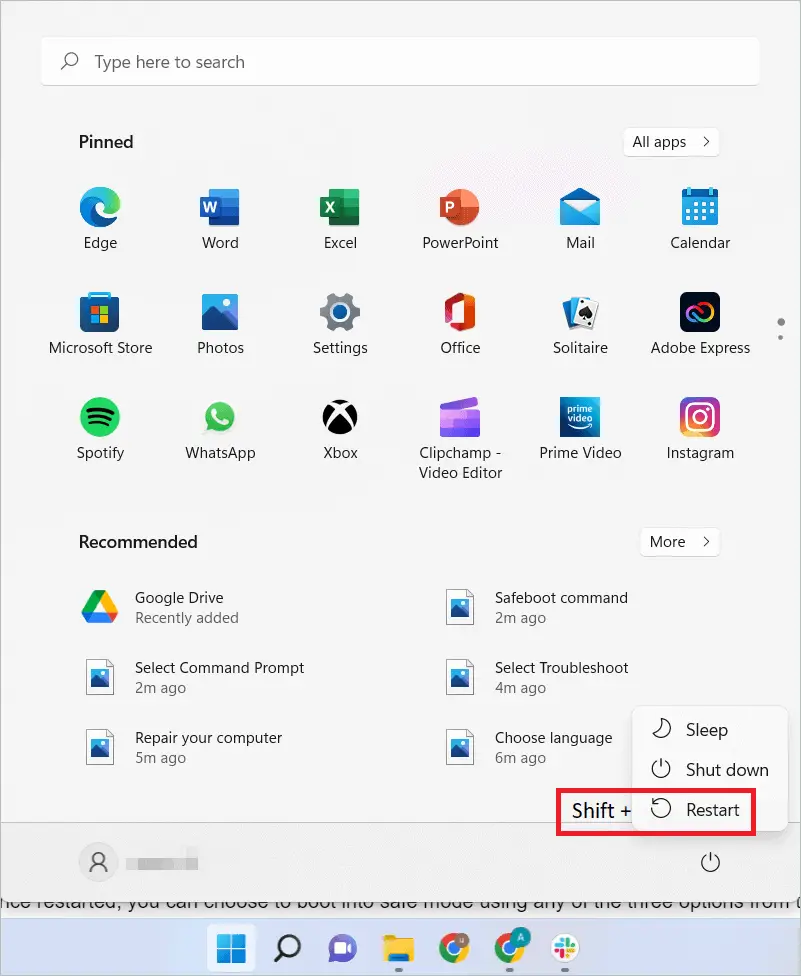
The OS restarts, and you will get the Choose an option window. Click “Troubleshoot.”
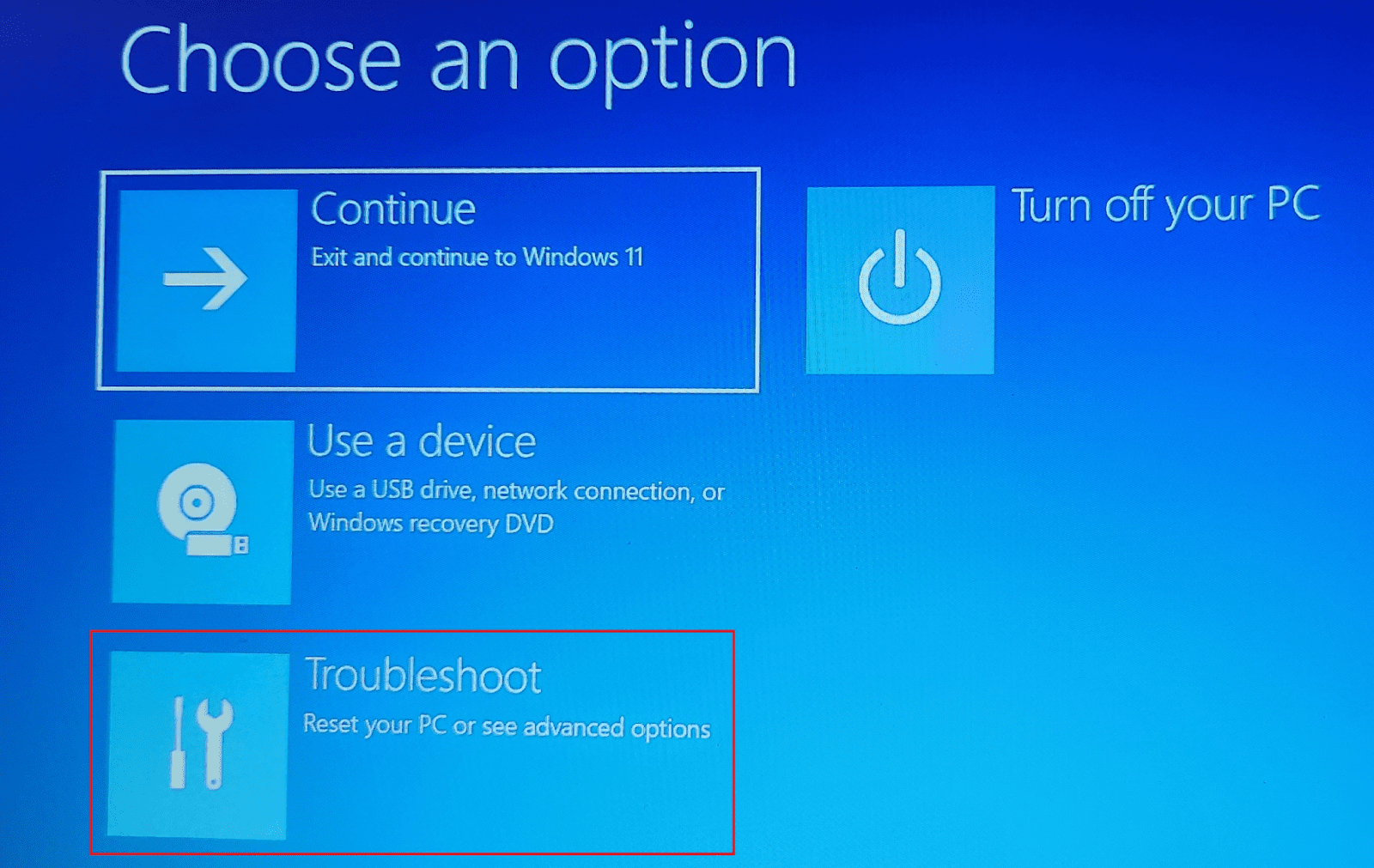
In the Troubleshoot window, click “Advanced options.”
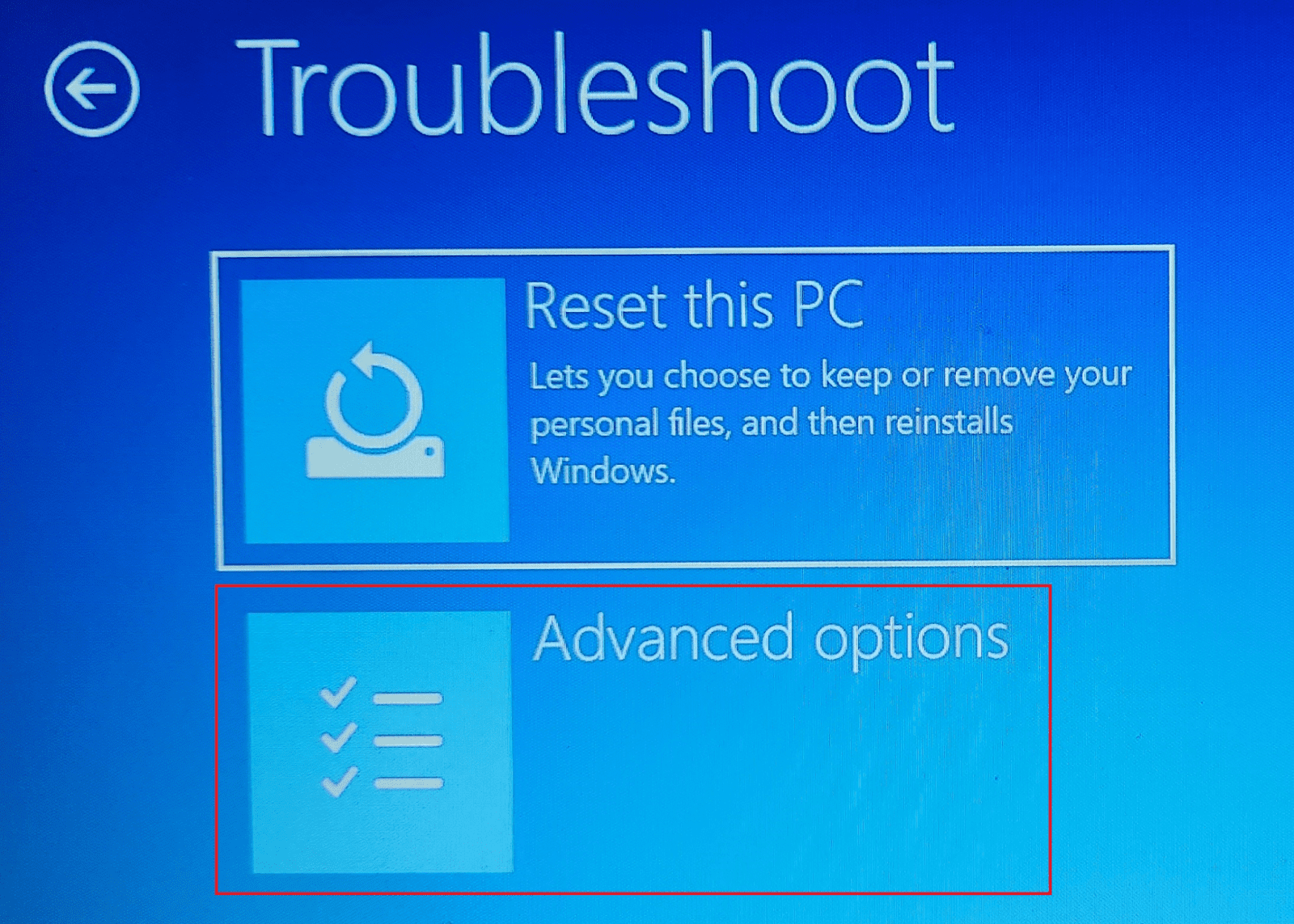
When the Advanced options screen loads, click “Startup Settings.” If this option is not visible, click “See more recovery options” to get it.
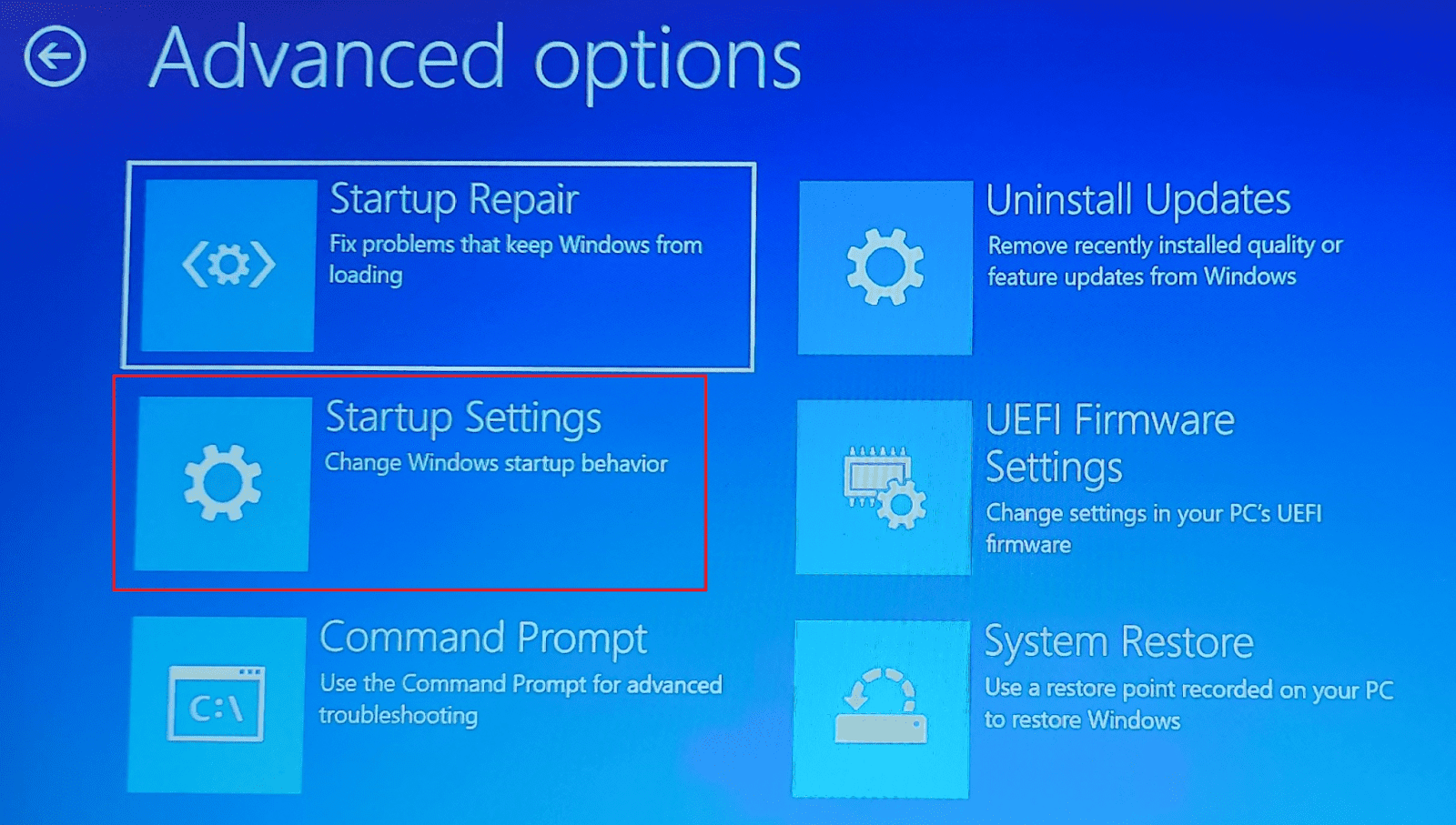
In the Startup Settings window, you will be notified that you can change Windows options after restarting. Click the Restart button.

Once restarted, you can boot into safe mode using any of the three options from the list.
Safe Mode: To enter the Standard Safe Mode option, press 4 or F4
Safe Mode with Networking: To load network drivers and services, press 5 or F5
Safe Mode with Command Prompt: To load Command Prompt automatically, press 6 or F6
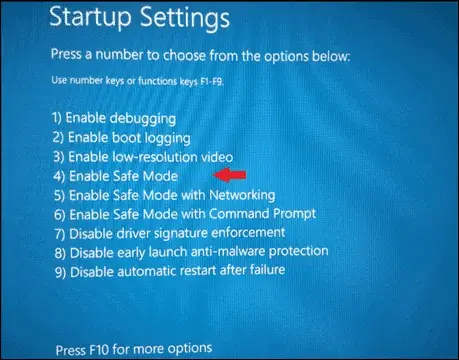
Choosing an option from the Advanced Boot Options will start Windows 11 in safe mode.
2. Boot Into Safe Mode In Windows 11 From The Sign-In Screen
Sometimes, you cannot sign into your PC and get stuck at the sign-in screen. Fortunately, we have a workaround for such situations. Like the previous method, you can press Shift and Restart together and start your PC in safe mode in Windows 11. Here is how.
See the power button icon in the bottom-right corner of the sign-in screen. First, press Shift and select the Restart option after clicking the Power icon.
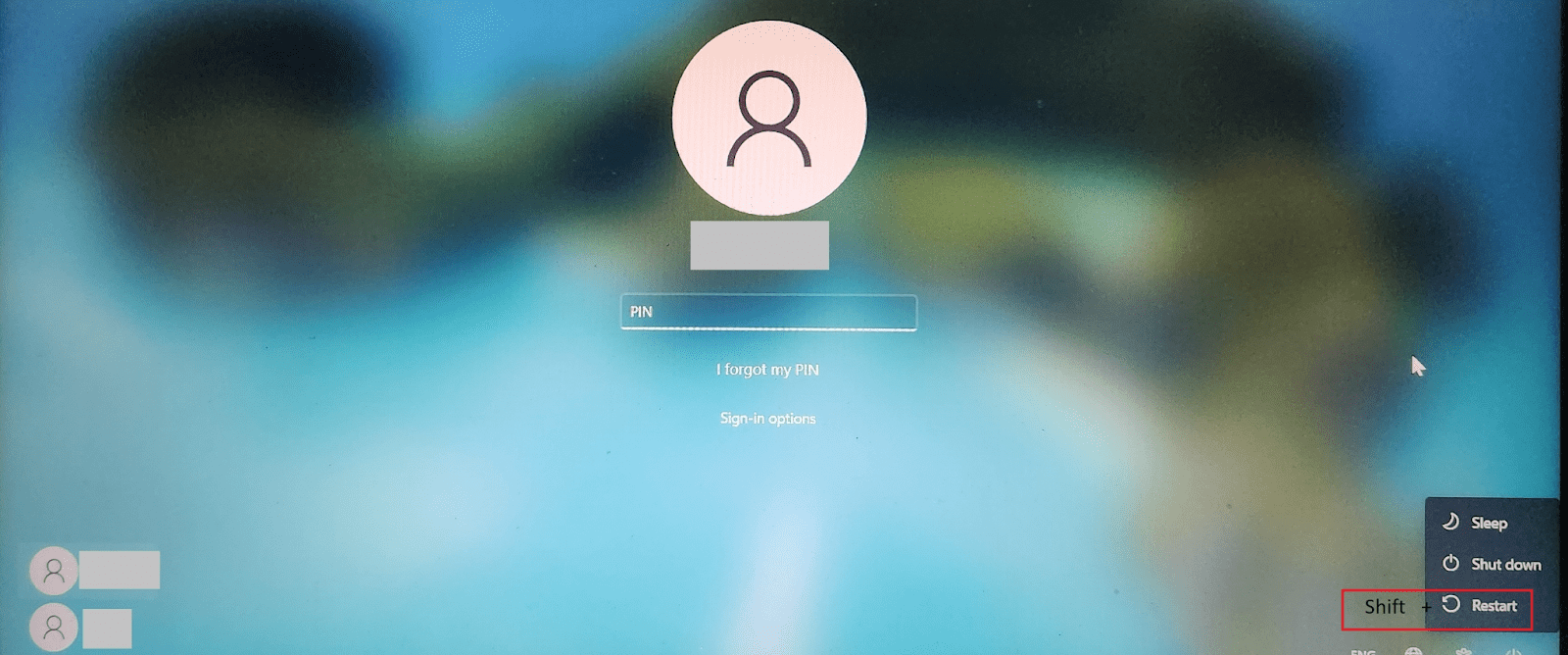
The system restarts and goes to the Choose an option window.
From here, go to Troubleshoot > Advanced options > Startup Settings. Now, press the Restart button. When the system restarts, you can opt for any safe mode type by pressing the corresponding key, as explained in the previous method.
3. Boot Into Safe Mode In Windows 11 by Forcefully Shutting Down the PC
Windows 11 has a built-in mechanism that goes to an advanced startup troubleshooting mode when some condition is met. You must stop your computer from starting in normal mode for this to happen. Don’t allow Windows to boot normally three times in a row, and it loads Automatic Repair Mode from where you can start safe mode in Windows 11. Follow the steps below to go to Automatic Repair Mode.
Press and hold the physical Power button for about 10 seconds to turn it off. Then, press it again to turn on the PC. When you see the manufacturer’s logo on the screen, press and hold the Power key for 10 seconds to turn it off. Now, press it to turn on the device and turn it off as you did before.
Now, the PC will restart into Automatic repair. Once the device is diagnosed, click “Advanced options” to enter the Windows Recovery Environment (WinRE). Finally, follow the instructions to go to safe mode.
Troubleshoot > Advanced options > Startup Settings > Restart. When the device restarts, a list of options appears. Press any of the keys depending on how you want to enter safe mode.
4. Using the Settings App
Entering safe mode from Settings is like a taken-for-granted option, as the Settings app is the go-to location for many tasks on your PC. Here are the steps to boot into safe mode in Windows 11 from the Settings window.
Type “Settings” in the search bar and open the Settings app.
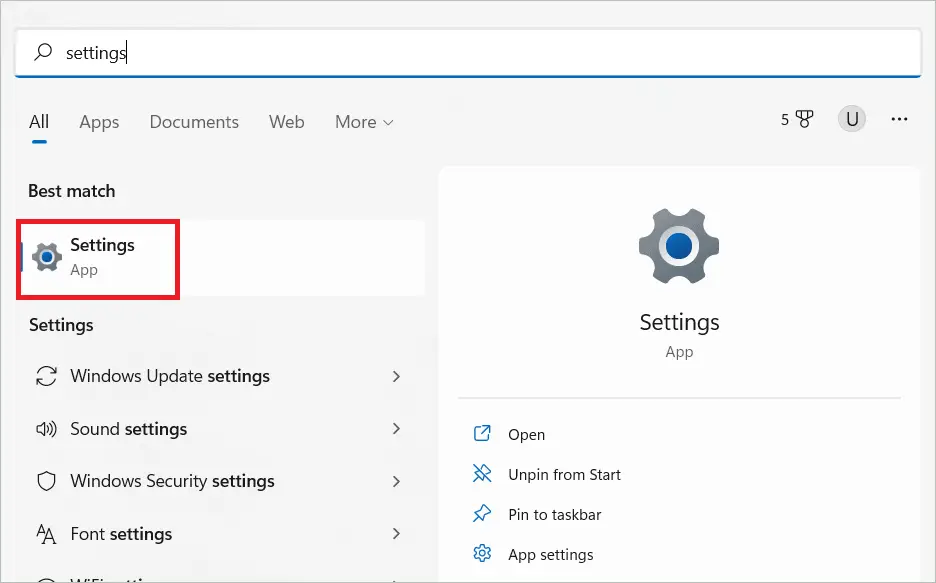
Select “System” in the left panel and “Recovery options” in the right.
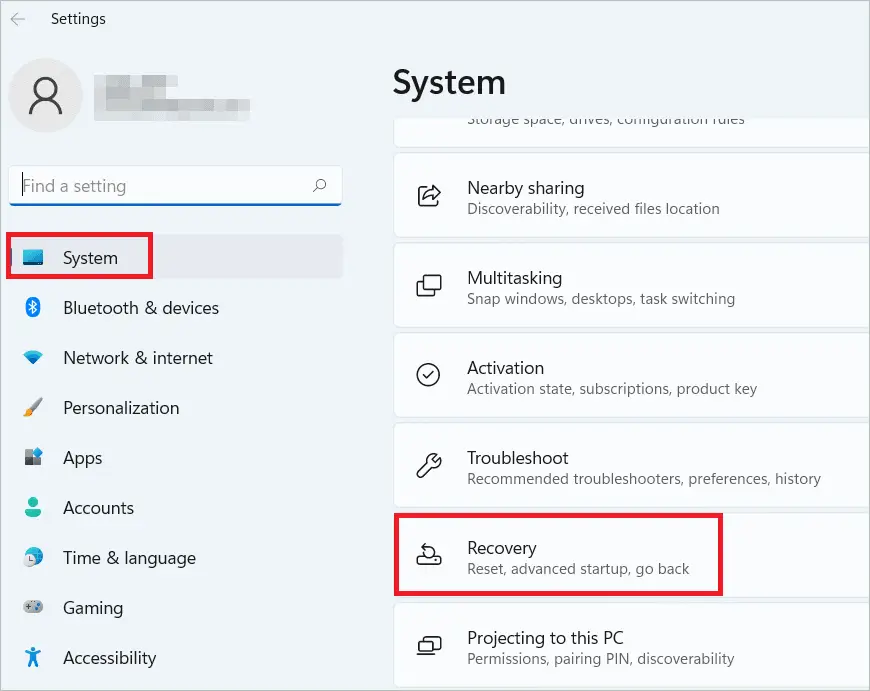
Click the “Restart now” button near the Advanced setup in the Recovery options section.
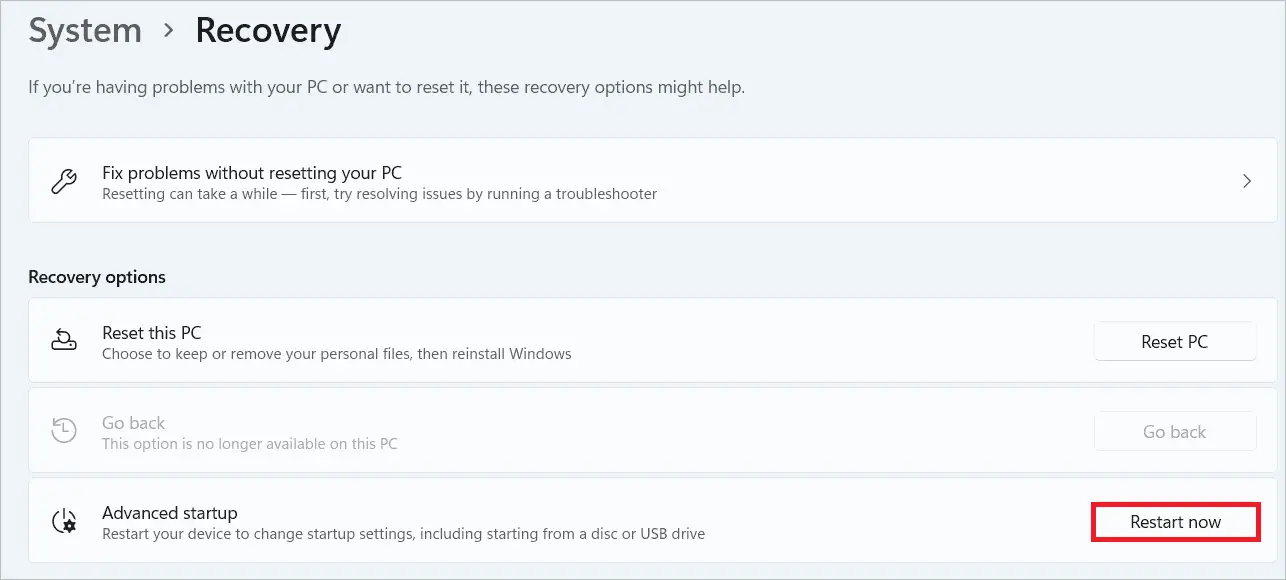
Click “Restart now” in the next window if you have saved your work.

After the system reboots, it shows you the Choose an option window.
Go to Troubleshoot > Advanced options > Startup Settings > Restart. Now, click any of the keys mentioned in the above methods to go to safe mode.
5. Using the Command Prompt
The shutdown command in the Command Prompt lets you enter safe mode in Windows 11. Even though this is an advanced version recommended for experienced users, it is as easy as any other method. So, look at how advanced users can execute the command in the CMD user interface and go to the recovery environment.
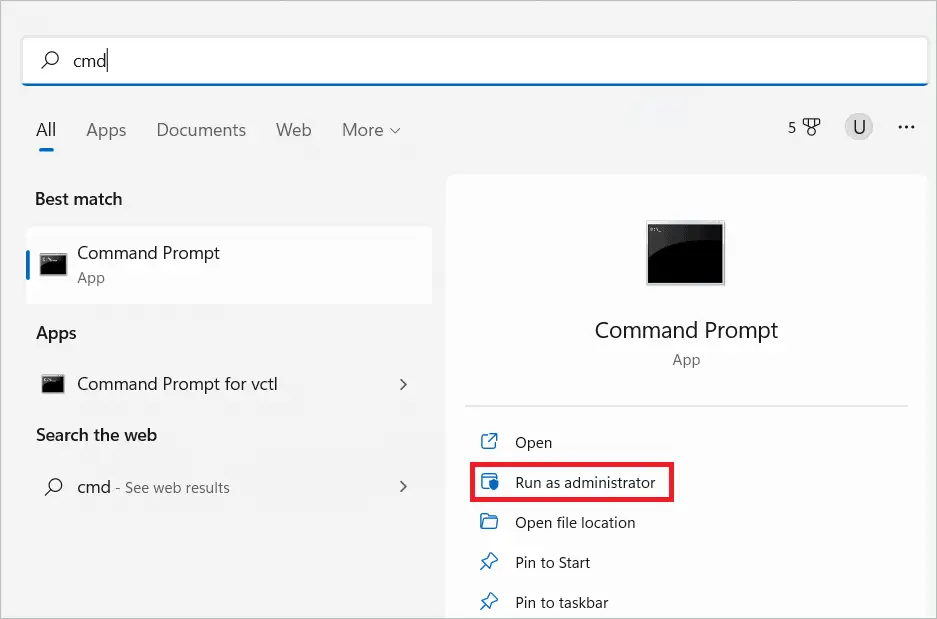
Type “CMD” in the search bar and click “Run as administrator.”
Type this command and press Enter.
shutdown.exe /r /o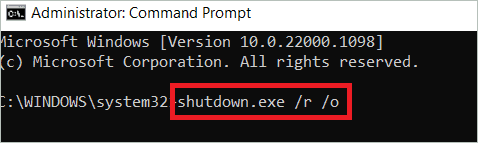
When the pop-up dialog box appears, click “Close.”
Now, the PC restarts and goes to the Choose an option window.
Go to Troubleshoot > Advanced options > Startup Settings > Restart. Now, click any of the keys mentioned in the above methods to go to safe mode.
6. Using System Configuration
System configuration or MSConfig utility helps users analyze and resolve the issues associated with the Windows startup process. The legacy MSConfig experience can be used to change the boot parameters and start safe mode in Windows 11. Let us see how we can do that.
Type “System configuration” in the search bar and open System configuration when it comes up.
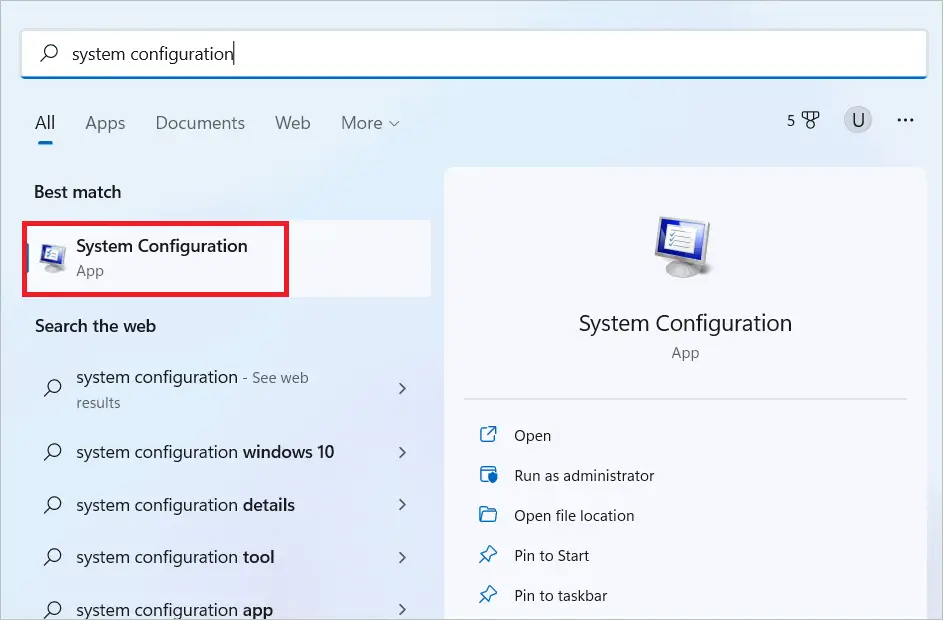
Select the Boot tab in the System configuration. Next, check “Safe boot” and click “OK.”
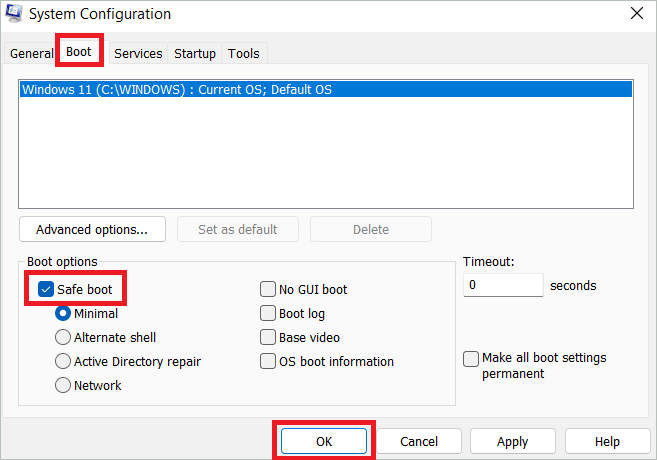
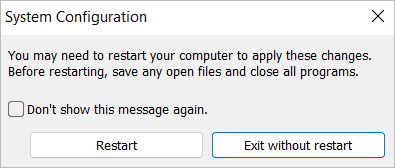
In the next window, select “Restart” if you want to start Windows 11 in safe mode immediately. Finally, select “Exit without restart” if you want to complete your work before restarting. The changes take effect once you restart.
Note: If you want to enter safe mode with networking, check “Safe boot” and select the “Network” radio button instead of “Minimal.” If you want to enter safe mode with Command Prompt, select the “Alternate shell” radio button.
7. Using a USB or DVD Installation Drive
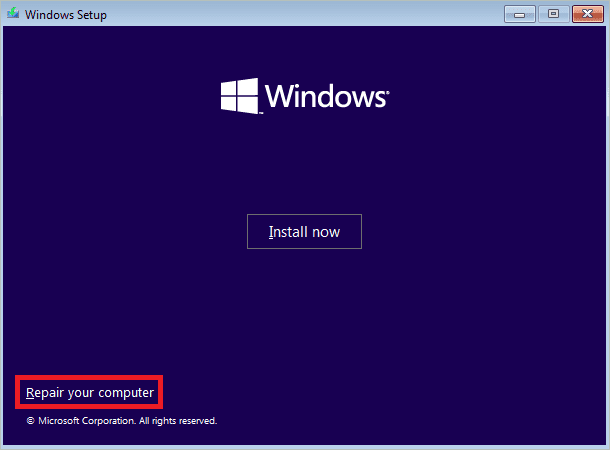
If you have a DVD or USB flash drive with the Windows 11 setup, you can use it to enter safe mode in Windows 11. You can start with the drive, and when the window for initiating installation appears, you must choose “Repair your computer” instead of “Install now.”
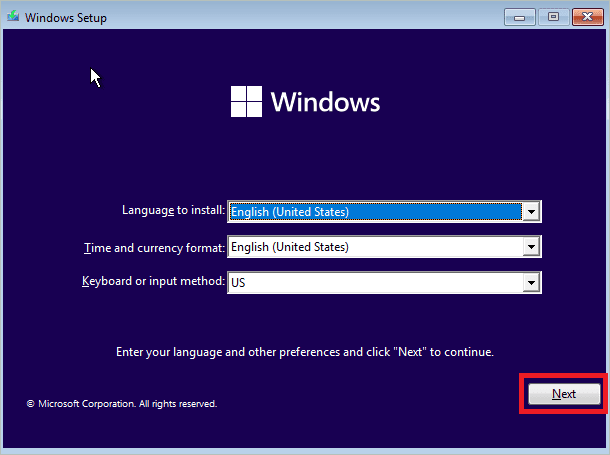
Boot your computer using the USB or installation drive, select the language and keyboard layout and click “Next.”
In the next window, click “Repair your computer,” seen in the bottom-left corner.
In the Choose an option window, click “Troubleshoot.”

On the Advanced options screen, click “Command Prompt.”
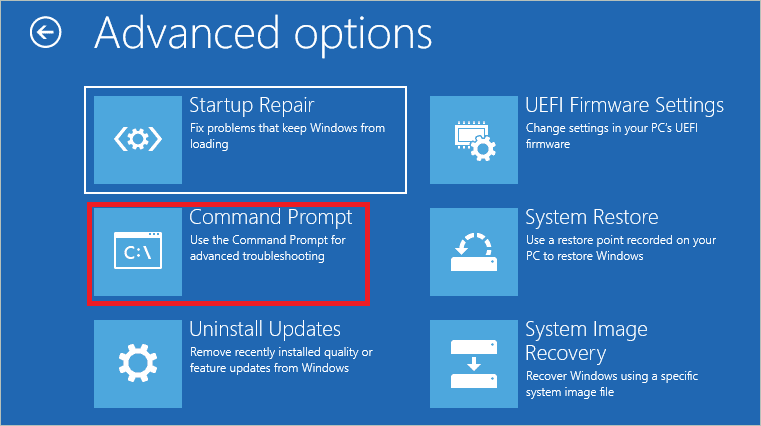
Execute the following command in the Command Prompt and press Enter.
bcdedit /s {default} safeboot minimal
You will get the following message: The operation completed successfully.
Now, close the Command Prompt window and select “Continue” in the Choose an option screen. The system will restart and enter safe mode.
Note: Once the issue is resolved, you can instruct Windows to start normally by running the following command in the Command Prompt.
bcdedit /deletevalue {default} safeboot8. Using a USB Recovery Drive
The last method uses a system recovery USB drive to boot into safe mode in Windows 11. There are no extra steps here, and this method is similar to the previous one. Let us see the steps here.
Boot your computer using the recovery drive and select the keyboard layout. You will be directed to the Choose an option screen.
Go to Troubleshoot > Advanced options > Startup Settings > Restart. Now, click any of the keys mentioned in the above methods to go to safe mode.
Exit Safe Mode in Windows 11
It can happen that even after solving the PC issue, your system still boots into safe mode in Windows 11. To enable your PC to start in the normal boot mode, follow the below steps.
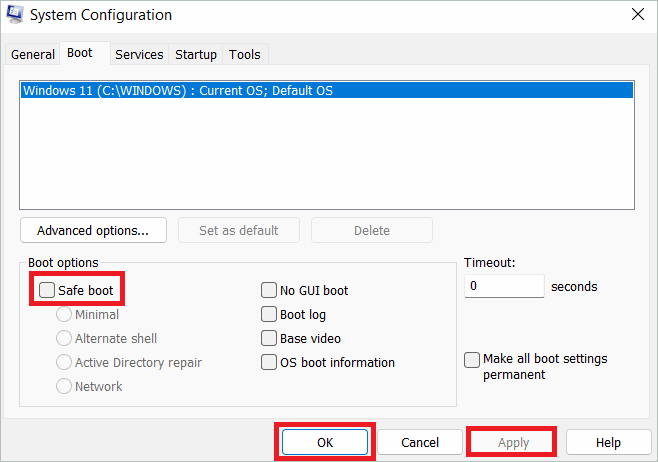
Open System Configuration and select the Boot tab. Uncheck the Safe boot option under Boot options. Then, click “Apply” and then “OK.” When you restart the computer now, it should boot normally.
Final Thoughts
Safe mode in Windows 11 offers a basic desktop experience with limited features. Booting into this minimal mode is a great way to unearth the issues caused by faulty drivers or bad software. If everything is working fine in the safe mode, you can ignore the basic drivers and focus on those causing the real issues.
You can enter either of the safe mode options, minimal safe mode, safe mode with networking, or safe mode with command prompt, to troubleshoot. Once you identify and rectify the problem, you can return to normal mode.







