Most users, when they consider buying a device, give a lot of importance to the size of the display. Another aspect of the display which is perhaps more important than the size is the type of display and the technology behind it.
The screen types, LED vs LCD vs OLED vs AMOLED vs PMOLED and its variants, in combination with the size of the display have a huge impact on your viewing experience. Doing the due diligence of knowing the different screen technologies and choosing the right one can ensure that you get the best value out of your new device.
Choosing the right one will enhance your viewing and user experience for a specific purpose you intend to use it for. So lets quickly try to understand the technology behind the screens and how you should choose the right screen type to suit your needs in the best way.
See More: How to Fix a Stuck or Dead Pixel on an LCD Display
Understanding LED vs Led and Other Display Tech
What is LCD and How Does it Work?
LCD is an acronym for Liquid Crystal Display.
LCDs have a multi-layer structure with a layer consisting of a liquid crystal material. The liquid crystals get illuminated when the fluorescent light falls on it and enables the viewer to see the image.
Used in Smartphones, Tablets, TVs, LCD screens, are made of six layers as explained below.
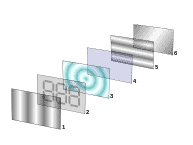
- The first layer is a polarizing filter that is filmed with the vertical axis that polarises the light.
- The second layer is a glass substrate with ITO (Indium Tin Oxide) electrodes with vertical ridges. The shapes of these electrodes are manipulated shapes that appear when LCD is turned ON.
- Twisted nematic liquid crystal is the third layer.
- The fourth layer comes as a glass substrate with a common electrode film (ITO) with horizontal ridges.
- The fifth one is the polarizing filter film with the horizontal axis.
- The last is a Reflective surface to send light back to the viewer.
Understanding TFT and IPS LCD Screens
There are two basic types of LCDs:
1. TFT LCD (Thin Film Transistor LCD)
TFT uses Thin Film Transistor technology to enhance image quality but tend to consume more power. This is used in TVs, computer monitors, and phones.
Its major drawback is that it offers quite poor viewing angles, and is best viewed a straight up-front angle. This drawback makes it less suitable for devices that require quality displays and also a variety of angles, like smartphones.
All its shortcomings were taken care of by the IPS LCD.
2. IPS LCD (In-Plane Switching Liquid Crystal Display)
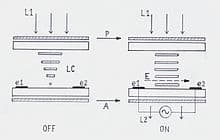
IPS LCD improves the performance of LCD technology and offers features that conventional LCDs were lacking in. The older LCD screens have a slow response time which can be a disaster if you are an avid gamer.
IPS LCD vs TFT LCD
IPS LCDs provide high contrast images compared to TFT LCDs, due to the presence of two transistors per pixel instead of one per pixel in the case of TFT. It also requires higher power to deliver sharp images that need stronger backlights, and thus IPS LCD screens consume more power than TFT LCD screens.
IPS LCD provides great white on the screen. IPS technology has improved over the years and thus you would come across acronyms like S-IPS (Super IPS), H-IPS (Horizontal IPS), P-IPS (Professional IPS) and AH-IPS (Advanced High-Performance IPS).
You would typically find the IPS LCD screen on Apple’s devices, including most of the iPads and iPhones up to the iPhone XR and iPhone 11.
The iPhone XS, XS Max, and iPhone 11 Pro devices have OLED displays, which we look into below.
What is LED and How Does it Differ From LCD?
Continuing our comparison between LED vs LCD, let take a look at how LED tech works. LED is an acronym for Light-Emitting Diode, which in itself does not tell us anything about the display technology. Technically, LED screens are “LED-backed LCD screens”, where the display panel itself is the same as that of an LCD, but with an array of light-emitting diodes used for the backlight generation.
What is the difference between LCD and LED screens?
Older LCD screens use fluorescent lamps for backlight, whereas the LED screen uses LEDs for the backlight. This is the primary difference between LCD vs LED screens.
Due to their brightness, they were used mostly in outdoor hoardings and these stay out in the Sun. The in-store signs are known as retailing signages and billboards and use these too. One can also see them being used in destination signs of public transport vehicles.
LED vs LCD: Which one is the better choice?
Being a more efficient technology, LED and the other improved versions of LED screens have become the defacto standard for high-end TVs, smartphones and other displays. LCD screens are also backed by LEDs instead of fluorescent lamps and are thus, basically, LED screens.
If you are comparing between LCD vs LED, the superior technology would be LED, or one of it’s improved variants mentioned below.
Now let’s take a look at the LED variants.
OLED vs LED: Which is a better Screen?
OLED is an acronym for Organic Light-Emitting Diode. OLED is fast becoming an interesting topic as far as more expensive screens are being discussed.
Unlike LCD and LED screens that leverage the LEDs generated backlight, OLED does not use any backlight. Instead, the screen has a layer of organic material that emits light when exposed to an electric current.
This helps to keep the screen panel as thin as possible and is capable of delivering the deepest levels of black since the light is produced individually for each pixel. As such, the pixels on an OLED screen are said to be ‘emissive‘ while those on an LED, which leverage a backlight, are said to be ‘transmissive‘.
An LED screen can draw lesser power, but The OLED screens have a richer display.
They also have the advantage of being thinner and flexible. In a comparison of LED vs OLED, I’d choose the OLED screen as it offers better quality and viewing experience.
OLED Variants: AMOLED vs PMOLED
There are two types of OLED displays – AMOLED and PMOLED.
Due to their differences and restrictions, AMOLED displays have become quite popular and commonly used in smartphones, while PMOLED has other limited uses.
PMOLED
PMOLED is an acronym for Passive Matrix Organic Light-Emitting Diode.
In a PMOLED screen, each row in the display is controlled sequentially. Since there is no storage capacitor, display pixels in each line are mostly off. A high voltage is required to give proper brightness to specific lines of the display to properly display content on it.
As such, the power consumption of PMOLED screens is high and becomes unsustainable for larger displays. This is a major difference between AMOLED vs PMOLED technology. Being more efficient by design, AMOLED supports large display sizes whereas PMOLED allows a display size of up to 3-inches only. As you would expect, AMOLED screens are also more difficult and costlier to manufacture.
AMOLED
AMOLED is an acronym for Active Matrix Organic Light-Emitting Diode.
AMOLED display uses a thin-film transistor backplane to directly access and switch each individual pixel on or off. This ultimately allows high-resolution picture quality and large screens. AMOLED displays are a way ahead OLEDs and use TFT technology.
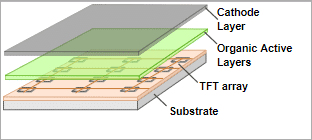
The AMOLED has an active matrix of OLED pixels that generate light when the electric current gets deposited on the TFT array; the TFT arrays then act as switches for the pixels.
The electric current flow is controlled by two TFTs at each pixel. One TFT starts or stops the charging of a storage capacitor. The second provides the voltage that is needed to create a constant current to the pixel.
There are several advantages of AMOLED:
- They can be used in any display size. (especially large ones.)
- It provides a great contrast level.
- They have an excellent refresh rate and high response time.
- Consumes less power.
- They provide great viewing angles and give a deep level of black to the images.
The AMOLED gives a dark black and inky level to the images that mean some part of the screen can be turned off. This ultimately consumes less power and gives good power efficiency.
But, if you want to view a full white screen on your AMOLED, be warned that it will consume more power.
AMOLED vs Super AMOLED: What is the Difference?
Super AMOLED is a Samsung-branded version of AMOLED. It is trademarked and can be used by Samsung only unless explicitly licensed out.
The differentiating factor of Super AMOLED is that it has a touch-panel integrated into the AMOLED layers instead of the top glass of the display panel. Not that other manufacturers do not have this technology, it is just that it cannot be called as Super AMOLED as that is a trademarked term of Samsung.
Further enhancements to this technology, like Super AMOLED Advanced and Super AMOLED Plus have come into existence. Pair them up with pixel density and you get an even wider variety of screen technology – HD Super AMOLED, HD Super AMOLED Plus, Full HD Super AMOLED or Quad HD Super AMOLED; all seen on various Samsung devices.
These variations resolve specific issues that plague a display, keeping the technology constantly evolving and are making the future aspect of AMOLED technology exceptionally bright and solid.
Conclusion
So now that we know a lot more about screens and what they are capable of doing, its easy to choose. Each technology has its merits and demerits.
AMOLED displays are best and used in a wide area because of the efficiency and great viewing angles. Furthermore, the high contrast level and support for large display size that it offers are also preferred.
As we found out, whites are great on IPS LCD whereas Blacks are better on AMOLED. Whatever the technology the manufacturers are using, they are striving to improve and enhance their present technology.
So, now you when you go to pick up any product with a display screen, understand what your priorities are and which screen-tech type suits you best.
Further Reading: How to Enable or Disable Adaptive Brightness in Windows 10







