Key Takeaways:
- Windows Defender is Microsoft inbuilt security feature that can protect the devices from vulnerabilities.
- Antimalware Service Executable is Windows Defender’s process that keeps running in the background to check any threats, viruses, or attacks.
- Continued running of this background process can lead to high CPU and memory utilization.
- You can modify the scheduling option to bring down the resource consumption of Antimalware Service Executable.
The Windows 10 computer can respond slowly if any process has high resource consumption. For example, many Windows 10 users complain about Antimalware Service Executable high memory usage after updating their PCs.
The Antimalware Service Executable, also known as MsMpEng.exe, is a Windows Defender service. It can have high CPU and memory consumption because it protects your computer from external threats. Also, if you perform a full scan on your PC to check for viruses, the Antimalware Service Executable can take up more than expected memory space. Therefore, it is essential to prevent high CPU usage and memory usage to avoid performance issues.
What is Antimalware Service Executable?
Antimalware Service Executable is a background service of Windows Defender. The Windows Defender is the built-in antivirus software of the Windows operating system. The Antimalware Service Executable (MsMpEng.exe) process tracks your activities and keeps the attacks or viruses away from your computer.
Continuous scanning increases the CPU and memory usage of your computer. However, some workarounds can help you keep your computer’s memory usage under control.
9 Solutions To Fix Antimalware Service Executable High Memory Usage
The below list of solutions can help you fix the Antimalware Service Executable high memory usage. In addition, you can perform the fixes in chronological order and get the issue resolved on your Windows computer.
1. Disable Real-Time Protection
You can disable real-time protection on your computer to temporarily resolve the high memory consumption issue. However, by doing this, the continuous scanning will be stopped, and your PC will be vulnerable to attacks. Therefore, proceed with caution and use this as a temporary resolution only.
Step 1: Press Windows key + I to open the “Windows Settings app” and go to the “Update & Security” section.
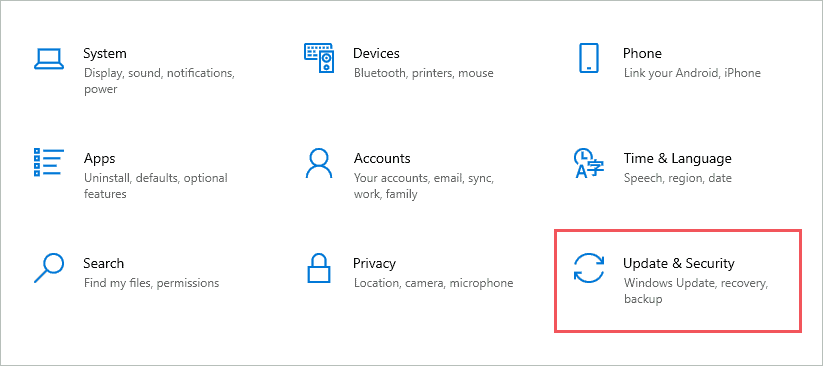
Step 2: On the left panel, click on “Windows Security.”
Step 3: Next, click on “Virus & threat protection” under Protection areas.
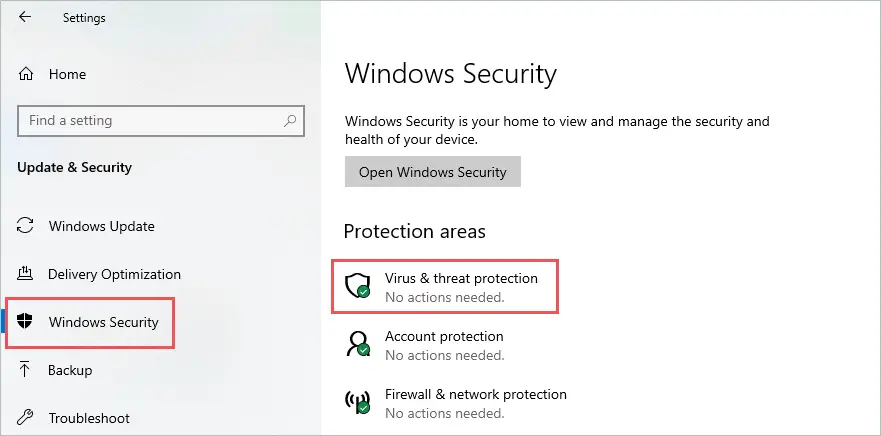
Step 4: Click on “Manage settings” under Virus & threat protection settings.
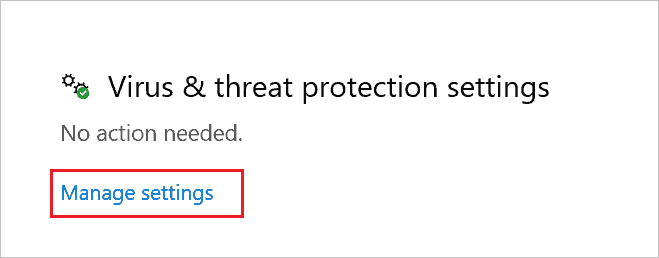
Step 5: Toggle the switch below “Real-time protection” to turn it off.

This will disable real-time protection on your computer.
You can now move on to other solutions to resolve Antimalware service executable high memory usage issues permanently. Once the issue is resolved, you can enable real-time protection on your PC again.
2. Modify Windows Defender Scheduling Options
You can change the Windows Defender Scheduling options to fix the Antimalware Service Executable high memory usage. When you change the scheduling settings, the resource consumption will go low. Thus, resulting in low memory usage as well.
Step 1: Press Windows key + R to open the “Run” window and type “taskschd.msc” there. Press the “Enter” key or click “OK” to open Task Scheduler.
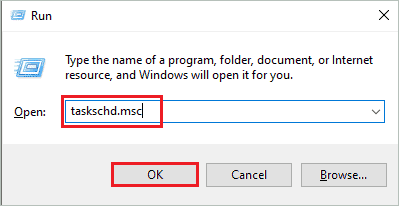
Step 2: In the Task Scheduler window, go to Task Scheduler Library ➜ Microsoft ➜ Windows from the left navigation pane.
Step 3: Now, under Windows, navigate to “Windows Defender” and double-click on “Windows Defender Scheduled Scan” from the middle frame.
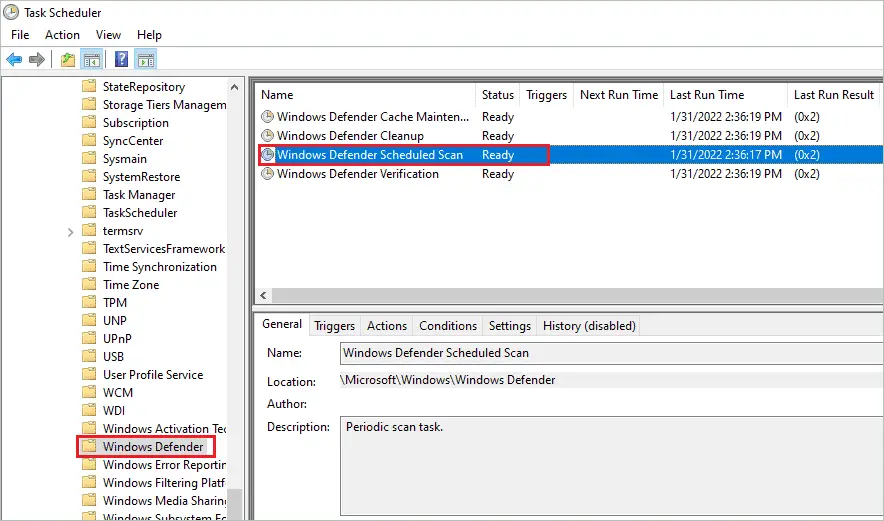
Step 4: In the Windows Defender Scheduled Scan Properties window, go to the “General” tab and uncheck the checkbox next to “Run with highest privileges.”
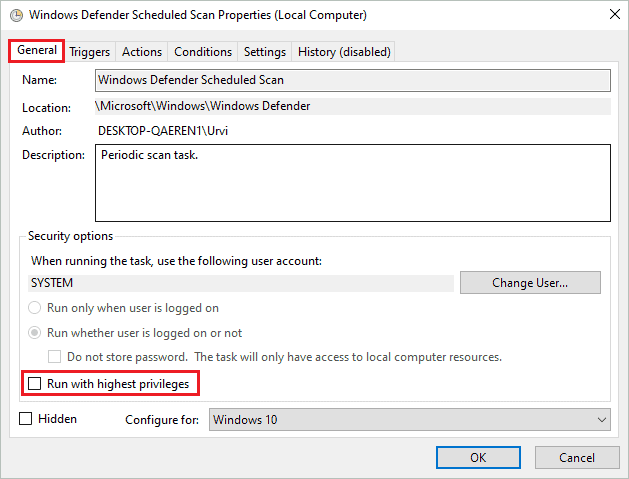
Step 5: Go to the “Conditions” tab and uncheck all the checkboxes. Click on “OK” to save the changes.
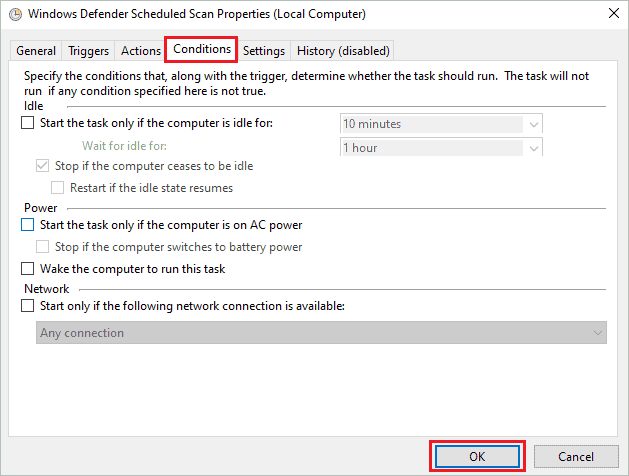
Now, you can manually trigger the scan schedule whenever you want. In this way, the scan can be done when your system is free.
To create a trigger, open the “Windows Defender Scheduled Scan Properties” again and go to the “Triggers” tab.
Next, click on “New.”
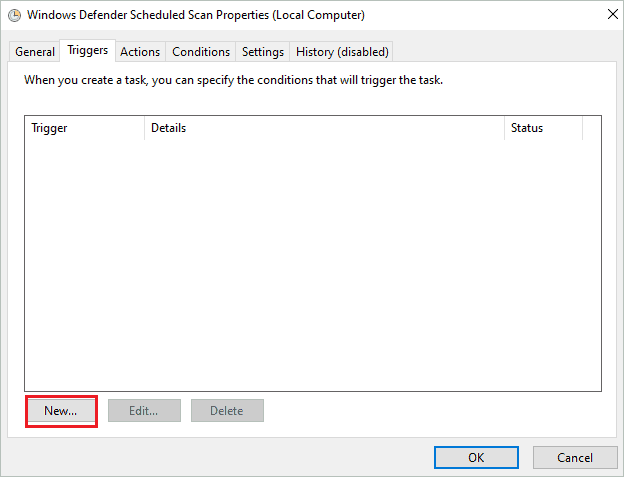
You can set the trigger as per your wish. Depending on your requirements, it can be one time, daily, monthly, or weekly.
Once the trigger is set, click on “OK” to save the changes.
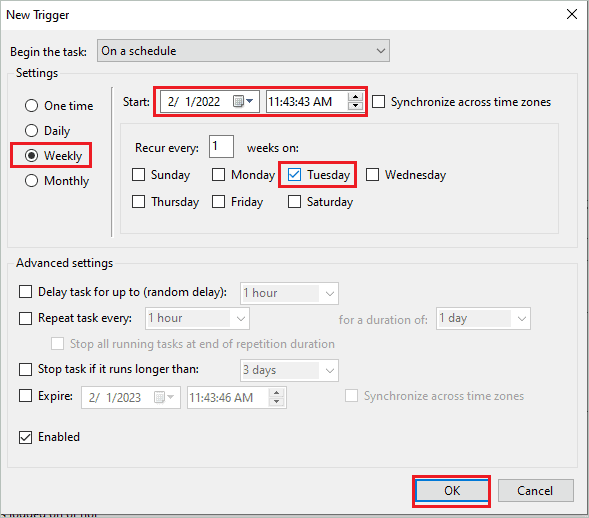
It will protect your PC against vulnerabilities and won’t use most of your memory and CPU.
3. Run SFC Scan
The corrupt system files can cause Antimalware Service Executable high memory usage on your Windows 10 PC. You can use Windows inbuilt utility called System File Checker (SFC) to scan and repair corrupted system files on your computer.
Open Command Prompt with administrator privileges on your computer and execute the sfc /scannow command as mentioned below.
sfc /scannow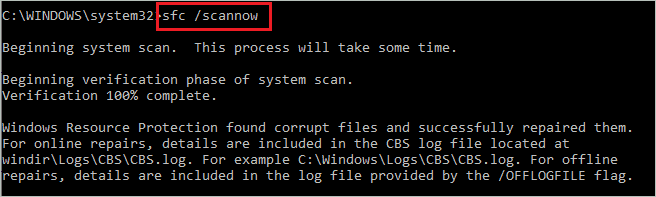
The command execution may take time, do not close terminal prompt in between the execution. Once the command is executed, reboot the computer and check if the Antimalware Service Executable high memory usage issue is resolved or not.
4. Add Antimalware Service Executable to Exclusion List of Windows Defender
If still Antimalware Service Executable shows high memory usage, you can add the process to Windows Defender’s exclusion list. This will resolve the issue for you.
You need to know the exact path of the process to add it to the exclusion list. Follow the simple steps below to add Antimalware Service Executable to the exclusion list correctly.
Step 1: Press Ctrl + Shift + Esc keys together to open “Task Manager.”
Step 2: In the Windows Task Manager, go to the “Processes” tab and right-click on the “Antimalware Service Executable” process.
Select “Open file location” from the context menu.
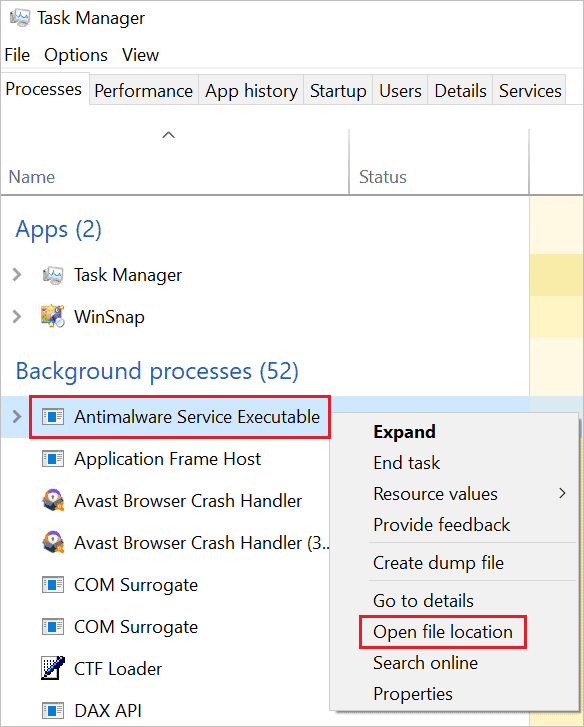
Step 3: Once the File Explorer window opens, copy the file path from the address bar and add the MsMpEng.exe file after it.
The path should look something like this:-
C:\ProgramData\Microsoft\Windows Defender\Platform\4.18.2111.5-0\MsMpEng.exe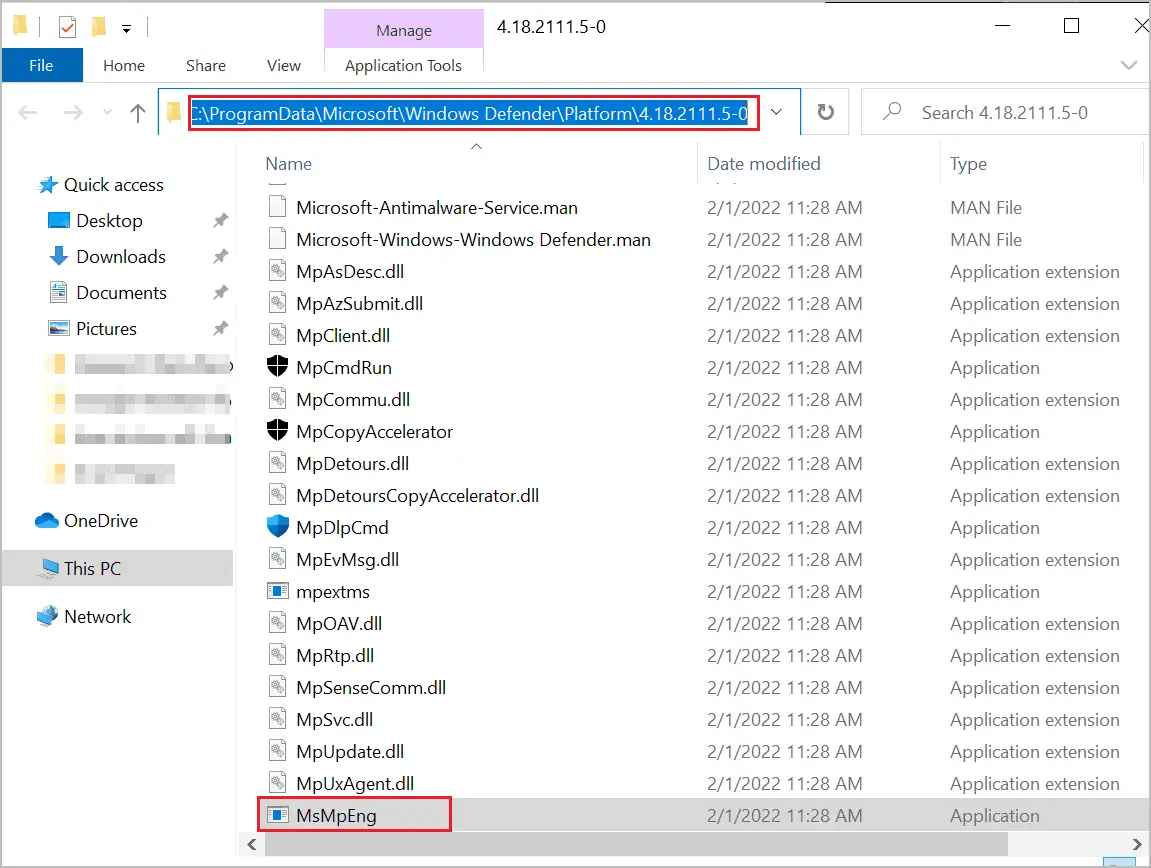
You can copy-paste the path in Notepad for future reference.
Note: The folder name with numbers may differ from system to system.
Step 4: Go to Settings app ➜ Update & Security ➜ Windows Security ➜ Virus & threat protection.
Step 5: Click on the “Manage settings” link under Virus & threat protection settings.
Step 6: Scroll down to the Exclusions section and click on the “Add or remove exclusions” link.
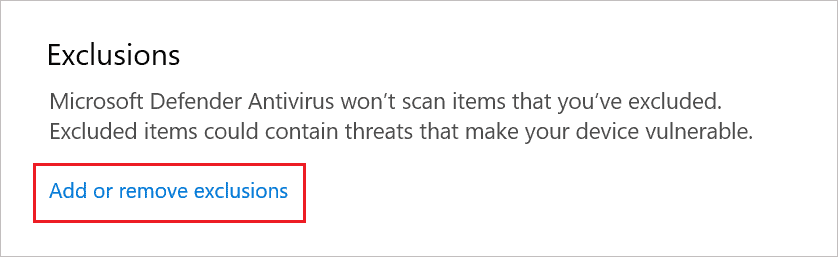
Step 7: Click on the “Add an exclusion” button and click on “Process.”

Step 8: In Add an exclusion dialog box, enter the path copied in Step 3 and click on “Add.”
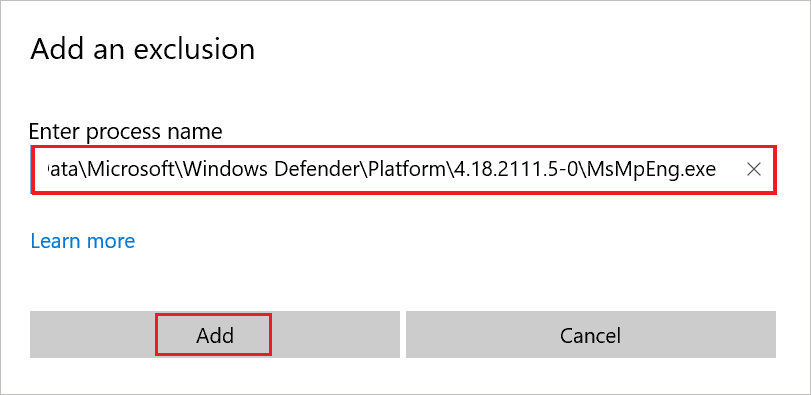
Once the exclusion is added, reboot your computer and check if the issue is resolved or not.
5. Perform a Full Malware Scan
If the viruses on your computer are causing Antimalware Service Executable to have high memory usage, you need to get rid of the viruses and malware.
You can use Windows Defender to perform the full scan or any trusted third-party antivirus software. The below-detailed steps are with respect to Microsoft Defender.
Step 1: Go to Settings app ➜ Update & Security ➜ Windows Security ➜ Virus & threat protection.
Step 2: Click on the “Scan options” link.
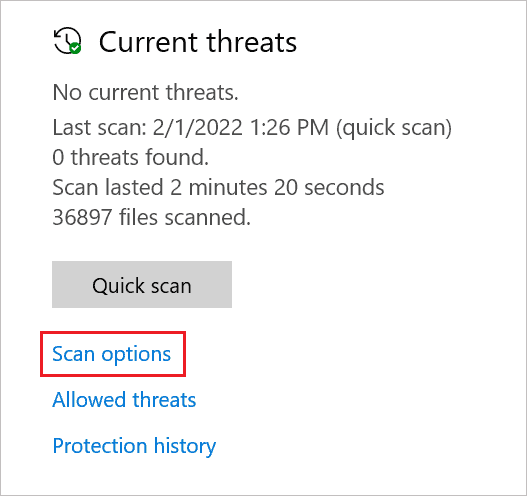
Step 3: Select the “Full scan” option and click on “Scan now” to begin with the scan.
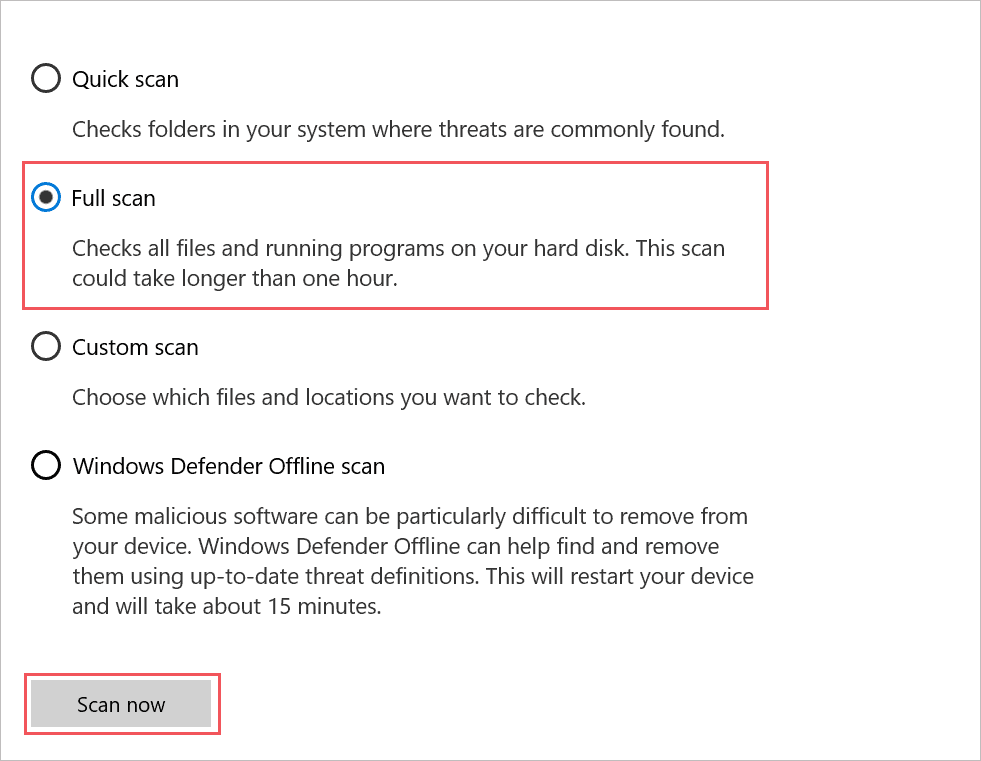
You can close all other applications and software while scanning your PC for viruses and malware. This will reduce the load on your CPU and memory usage.
6. Update All Device Drivers
The outdated device drivers can also cause processes to consume high memory usage. You can update all the device drivers on your PC.
The drivers can be updated manually from the Device Manager. First, however, make sure you download the stable version of driver software from a trusted source.
You can also use driver updater software like Driver Booster to update the drivers automatically. Once the driver is updated, check if the issue is resolved or not.
7. Roll Back Windows Defender
You can experience Antimalware Service Executable high memory usage because of a bad update of Windows Defender. Simply rolling back the update can help you resolve the issue on your Windows PC.
Press Windows key + S and search for cmd in the search box. Then, click on “Run as administrator” for Command Prompt.
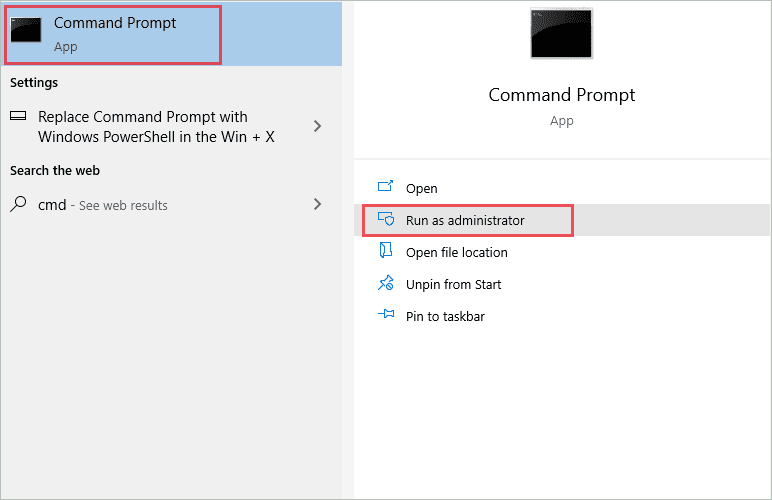
Once the elevated Command Prompt launches, execute the below command
"%PROGRAMFILES%\Windows Defender\MPCMDRUN.exe" -RemoveDefinitions -AllAfter executing the above command, run the following command to remove the recent Windows Defender update.
"%PROGRAMFILES%\Windows Defender\MPCMDRUN.exe" -SignatureUpdateNow, reboot your computer and then check if the high CPU and memory usage issue is resolved or not.
8. Disable Windows Defender from Registry Editor
If the Windows Defender background process is consuming high memory, you can disable Windows Defender via Registry Editor to resolve the issue.
Step 1: Press Windows key + R to open “Run” and type “regedit” there. Click OK to open the “Registry Editor.”
Step 2: In the Registry Editor, navigate to the below-mentioned path.
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Policies\Microsoft\Windows DefenderStep 3: In Windows Defender, search for “DisableAntiSpyware.” If you don’t find it, right-click on the Windows Defender folder and select New ➜ DWORD (32-bit) Value from the context menu.
However, if you find it, you can move on to the next step to modify the Value data of DisableAntiSpyware registry entry.
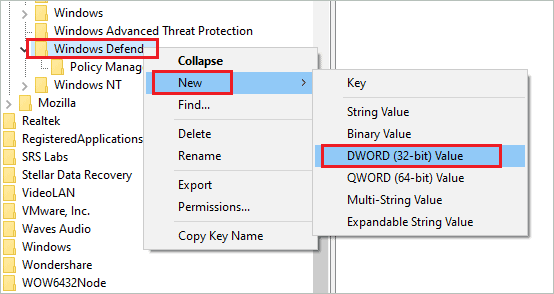
Step 4: If you created DisableAntiSpyware or it is already present, performing the following step is mandatory.
Double-click on DisableAntiSpyware and change its Value data to 1 to disable Windows Defender.
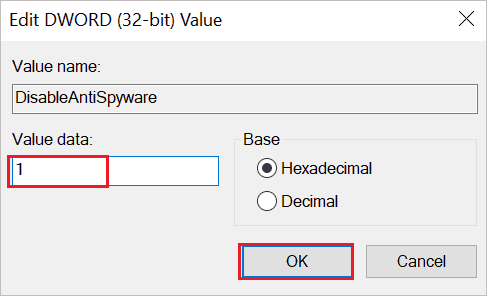
You can reboot the PC and check if the issue is resolved or not.
9. Use Trusted Third-party Antivirus
If Windows Defender services are still taking up your CPU and memory, you can use any trusted malware removal tool. Well, third-party antivirus software offers many features and can protect your computer from vulnerabilities. With a trusted antivirus program, you can keep attackers, viruses, and malware infections at bay.
However, make sure you download the antivirus software from an official source; otherwise, you can end up installing malware on your computer.
Conclusion
Sometimes, the background processes can consume high PC resources. You can either forcibly end such processes. However, this is not always the solution, as some processes are critical for PCs and need to run in the background. For example, the Antimalware Service Executable is the background process for Windows Defender and can have high memory and CPU usage in Windows 10 PCs.
Well, this process is crucial for saving your computer from malware attacks and hackers. You can perform some fixes and workarounds to resolve this issue. The above guide lists solutions that can help you resolve Antimalware Service Executable high memory usage problems in Windows 10.
FAQs
Can I end Antimalware Service Executable in the Task Manager?
You can end Antimalware Service Executable in the Task Manager, but it will start again once you reboot the PC. If this Windows Defender antivirus process takes up too many resources, you can modify the scheduling settings to reduce resource consumption.
How do I stop Antimalware Service Executable from using so much memory?
You can disable real-time protection, modify Windows Defender scheduling options, run SFC scan, add the service to the exclusion list, perform a malware scan, update drivers, roll back Windows Defender update, disable Windows Defender or use third-party antivirus software to stop Antimalware Service Executable from using so much memory.







